Schema Electrique Typhoon Bois Eco Concept Fr My XXX Hot Girl
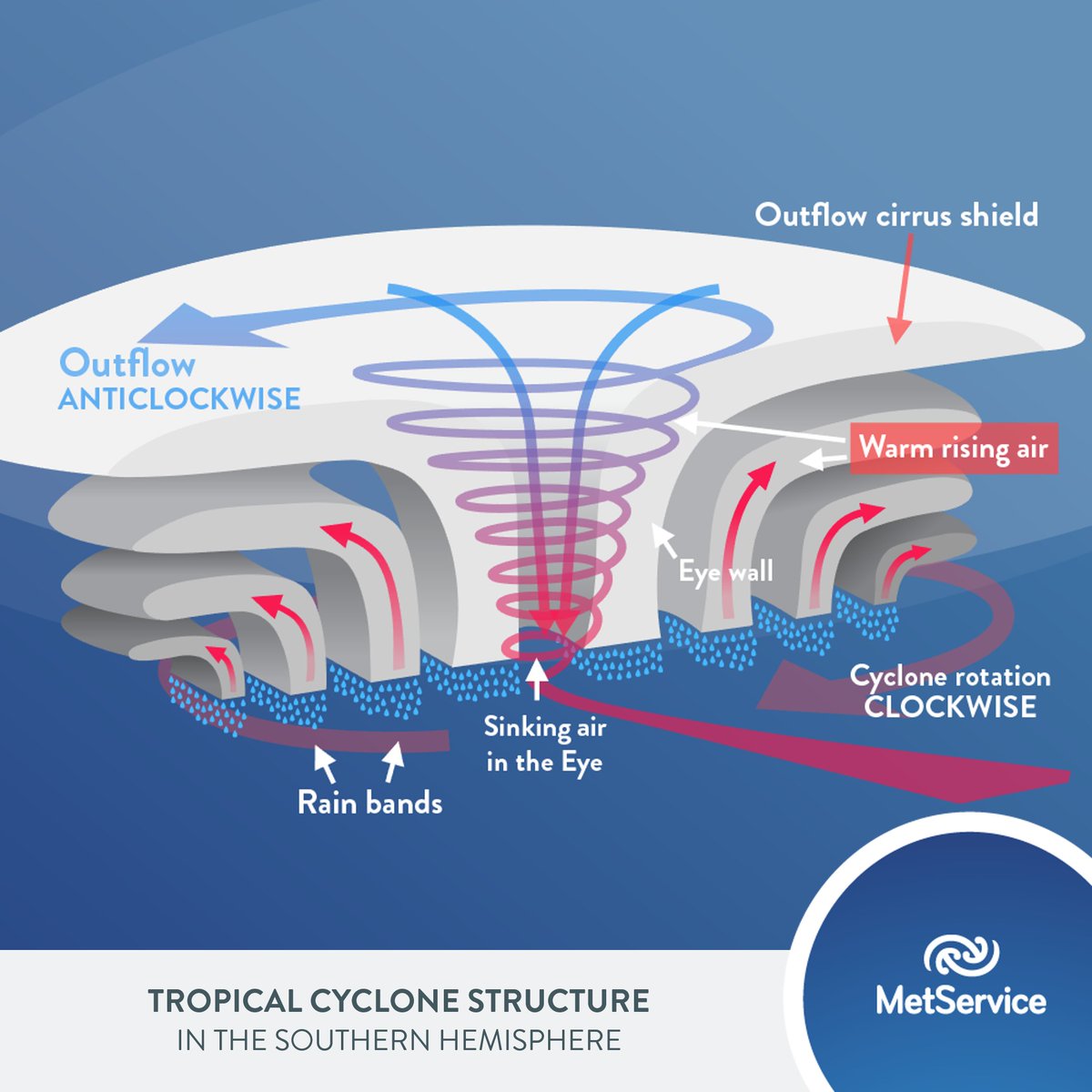
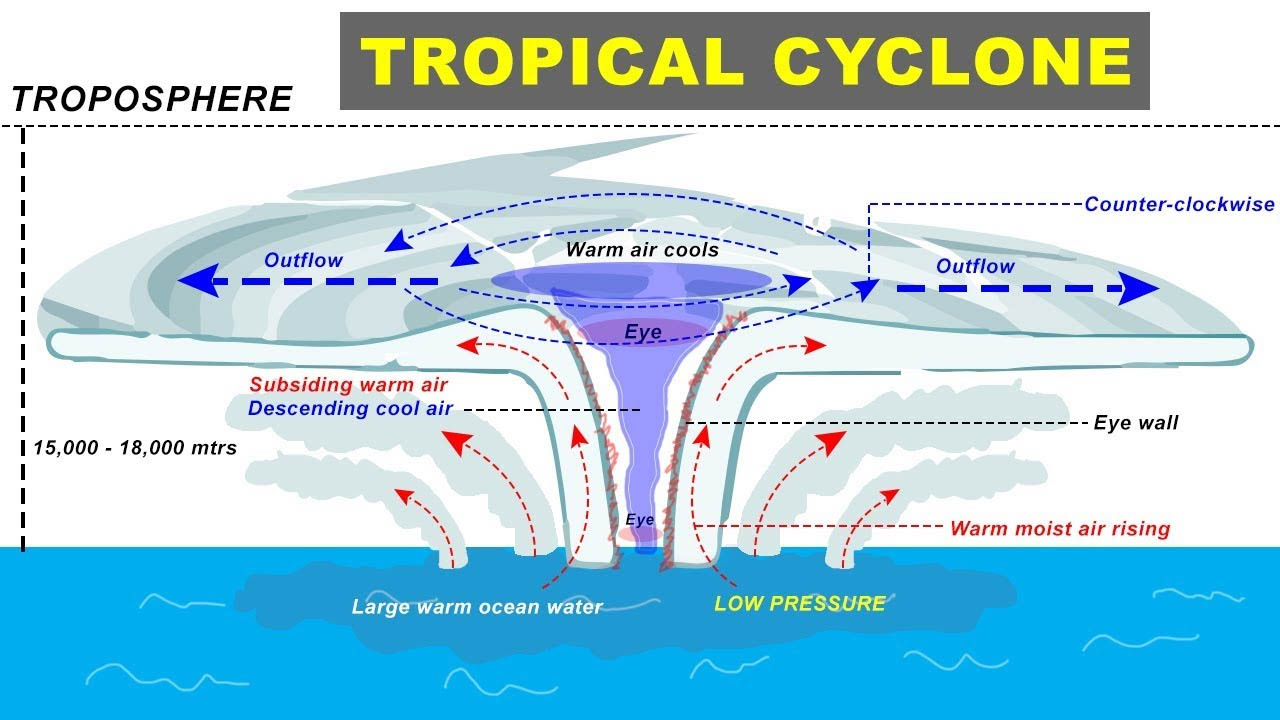
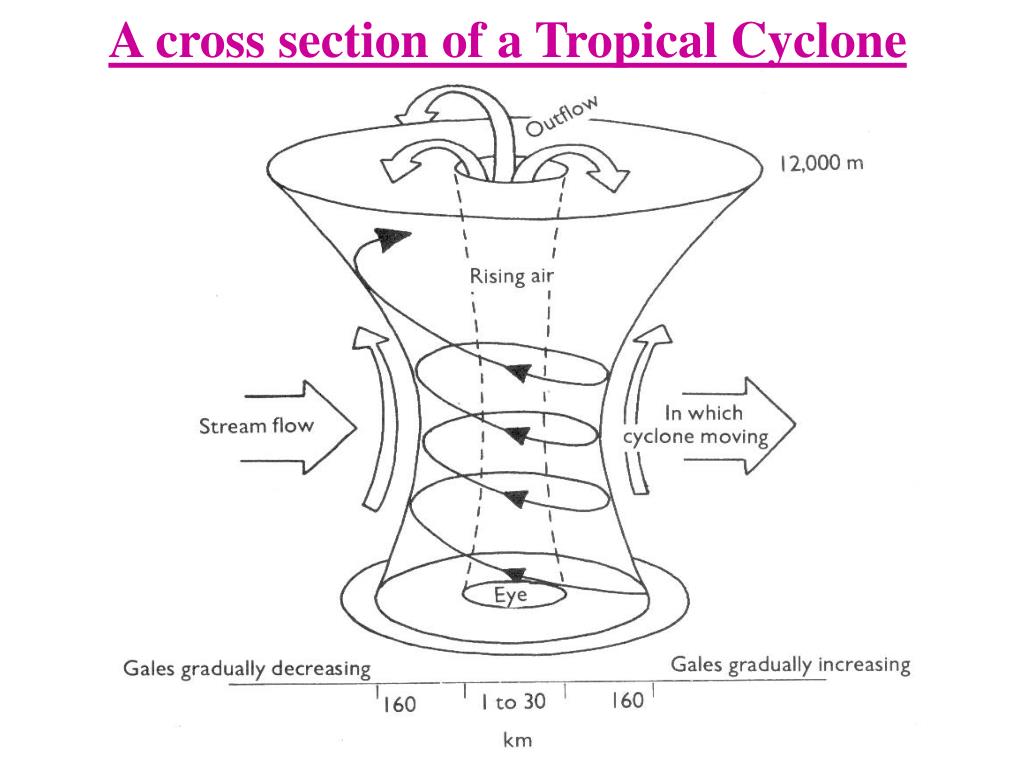
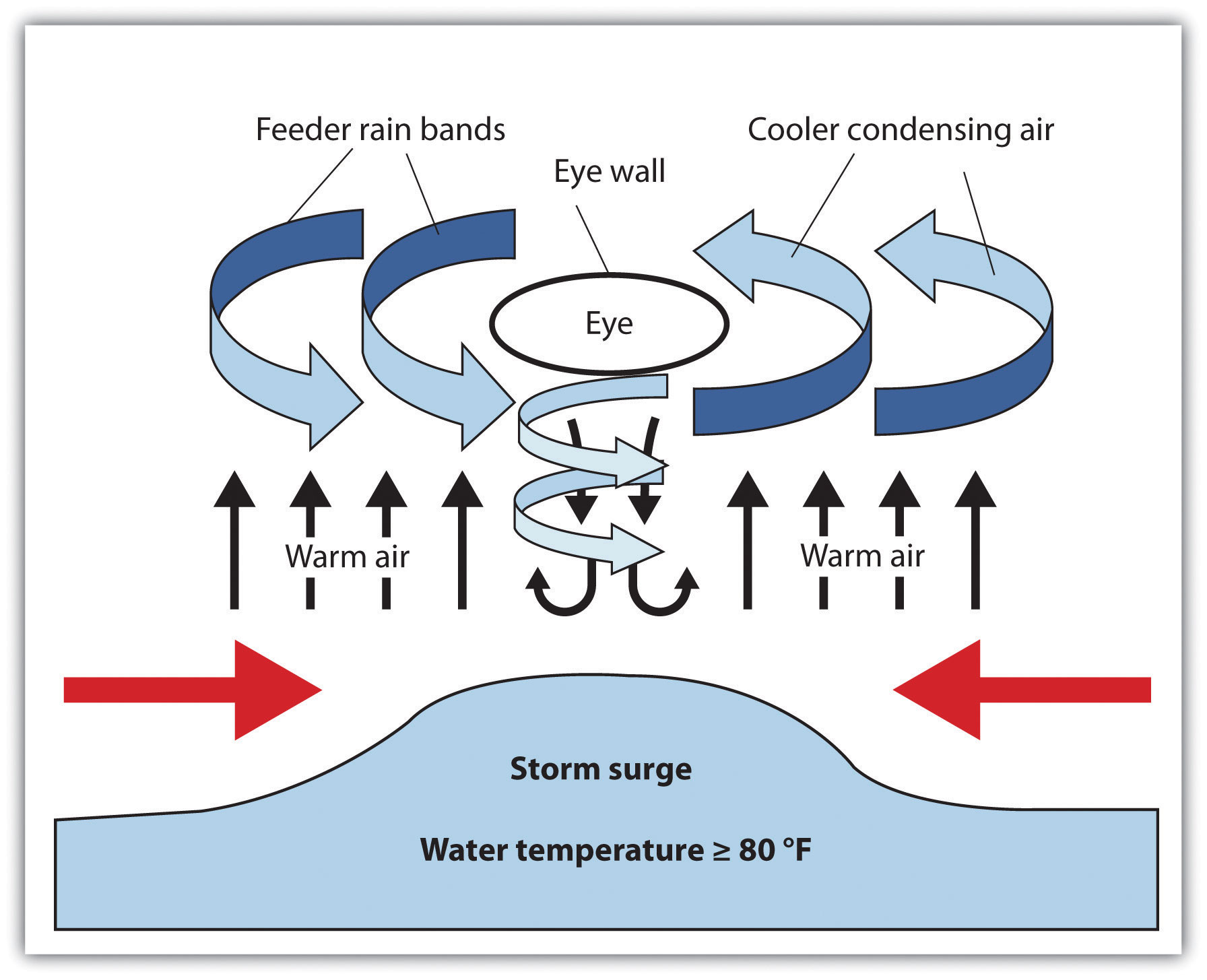
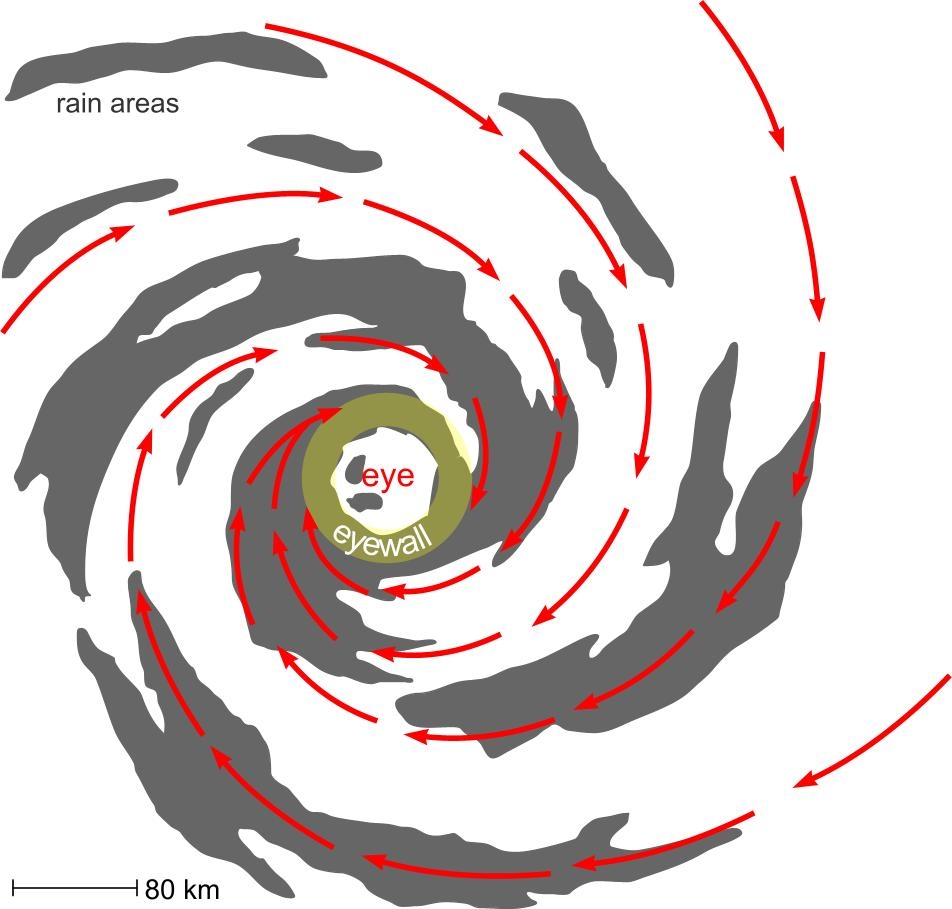
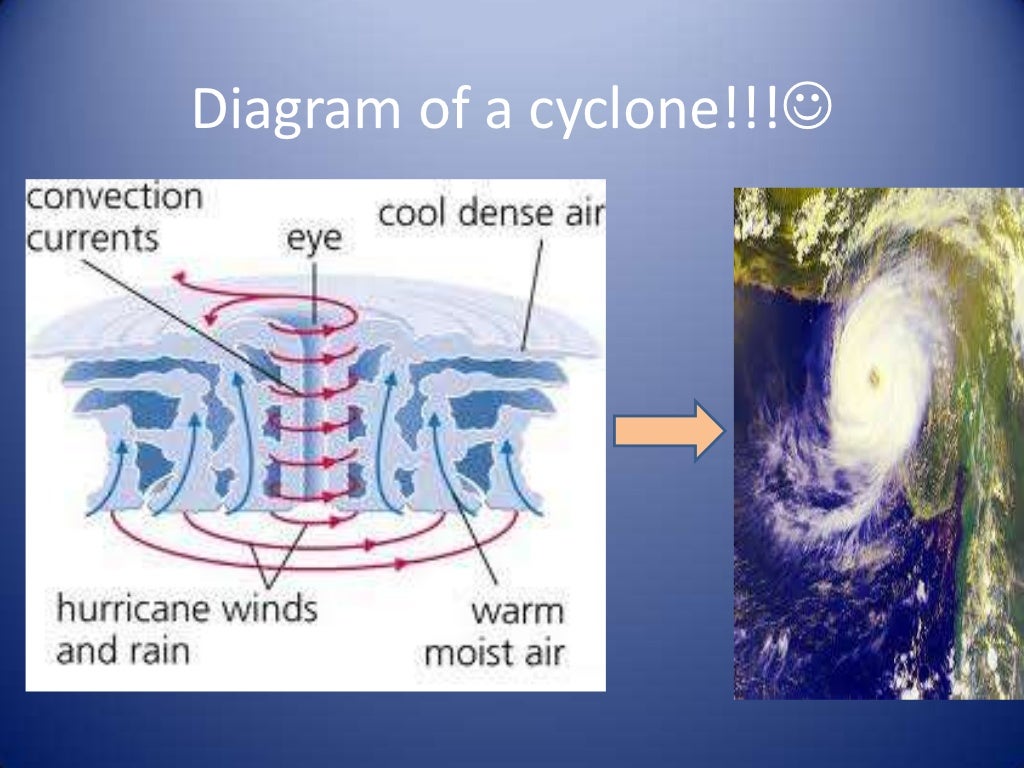
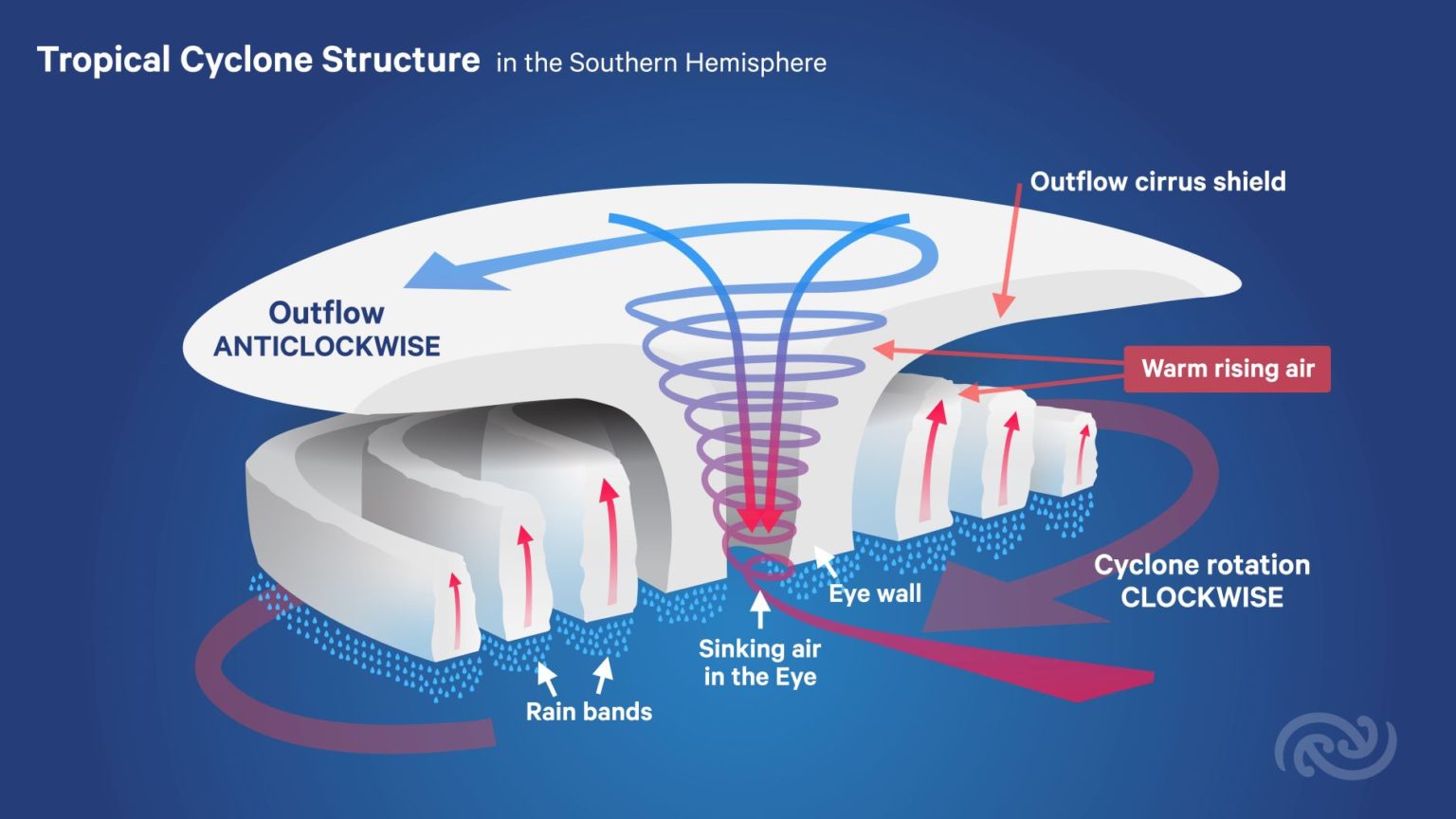
Tropical Cyclone Structure. The main parts of a tropical cyclone are the rainbands, the eye, and the eyewall. Air spirals in toward the center in a counter-clockwise pattern in the northern hemisphere (clockwise in the southern hemisphere) and out the top in the opposite direction. In the very center of the storm, air sinks, forming an "eye.
What are Tropical Cyclones and their characteristics? Geography4u read geography facts, maps
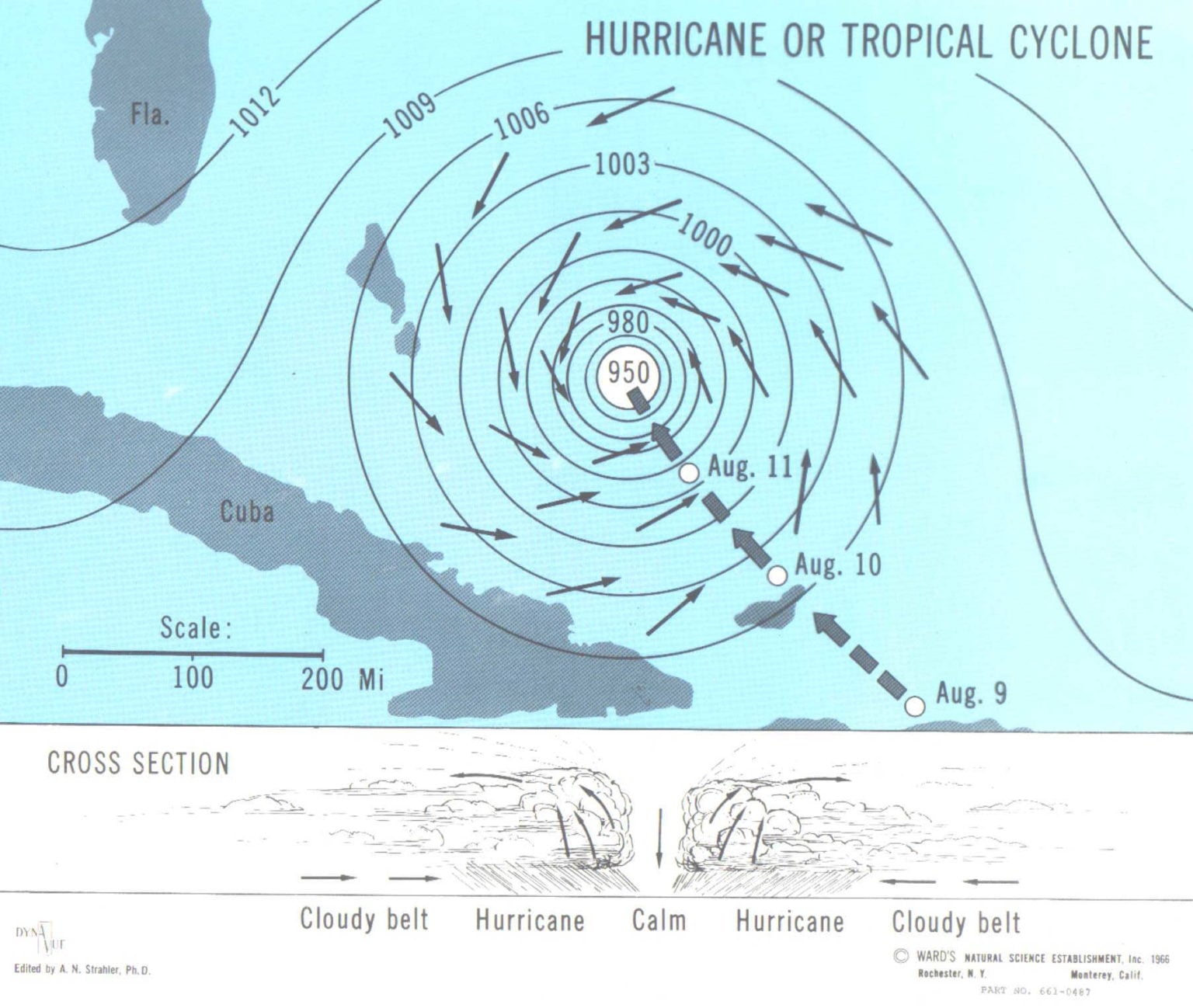
tropical cyclone, an intense circular storm that originates over warm tropical oceans and is characterized by low atmospheric pressure, high winds, and heavy rain. Drawing energy from the sea surface and maintaining its strength as long as it remains over warm water, a tropical cyclone generates winds that exceed 119 km (74 miles) per hour.
tropicalcyclone
Diagram of a tropical cyclone system Rising seas lead to storm surges As well as damaging winds, a tropical cyclone can cause the sea to rise well above normal tide levels when it comes ashore. These storm surges are caused by strong, onshore waves or reduced atmospheric pressure—or both.
Tropical Cyclones 101 What Exactly Is A Tropical Cyclone? Weather.us Blog
But Did You Check eBay? Check Out Top Brands On eBay. Over 80% New & Buy It Now; This Is The New eBay. Find Great Deals Now.
PPT WEATHER MAPS PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID7060658
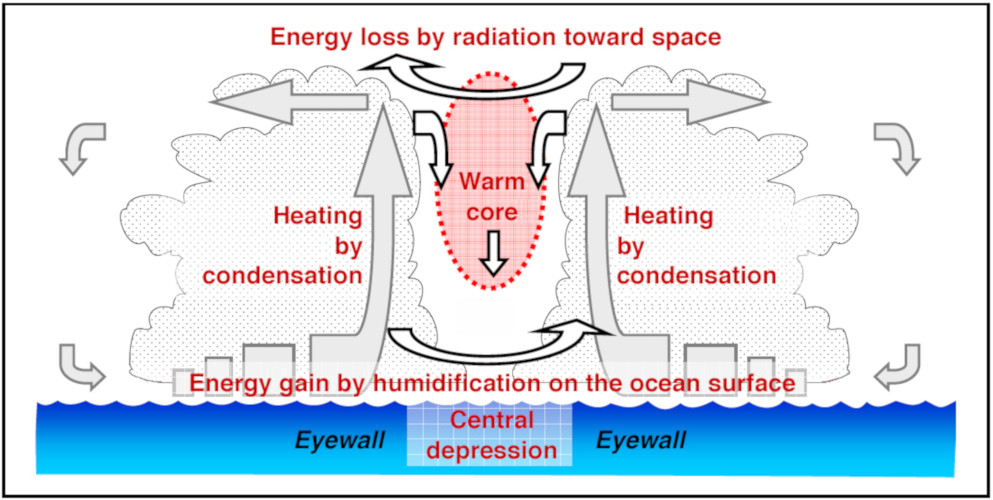
A view from space (see following diagram) allows a fuller appreciation of the majestic nature of tropical cyclones. A closer look can bring out further details. The bright patch near the storm centre is the cirrus canopy - high clouds emanating outwards from the top of the centre.
Tropical Cyclone Diagram
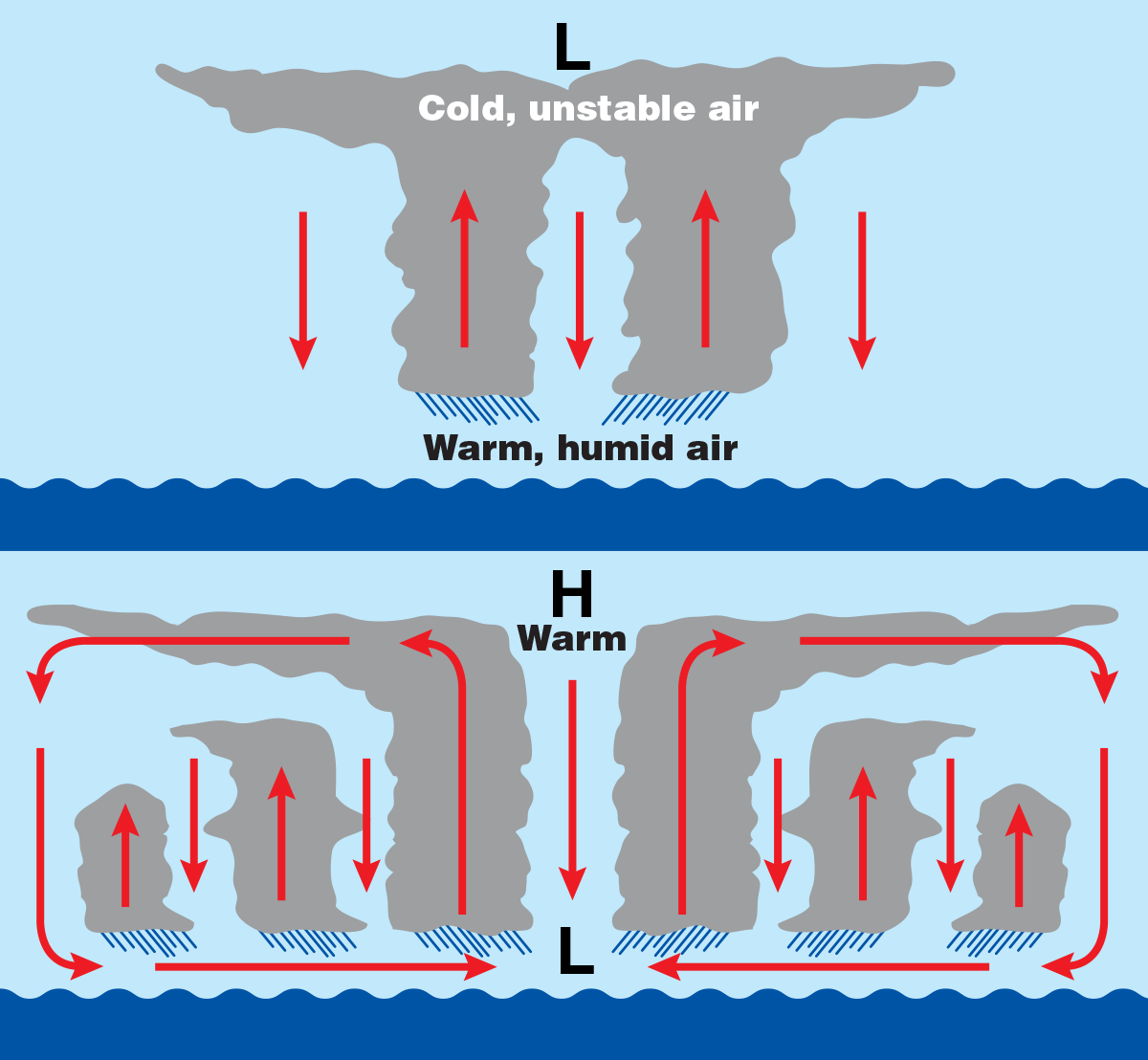
Tropical cyclones are made of thunderstorms. Near the center ( core) of the tropical cyclone is a ring or circle of thunderstorms called the eyewall. This is the most violent part of the storm with the heaviest rain and the greatest radar reflectivity (Fig. 16.2). The tops of these thunderstorms can be in the lower stratosphere: 15 to 18 km high.

tropical cyclone Kids Britannica Kids Homework Help
¡Precios increíbles y alta calidad aquí en Temu. Envío gratuito en todos los pedidos. ¡Solo hoy, disfruta de todas las categorías hasta un 90% de descuento en tu compra.
Tropical Cyclones (Hurricanes)
A tropical cyclone is a circular storm that forms over warm oceans . When a tropical cyclone hits land, it brings heavy rains and strong winds . The winds can destroy buildings and rip out trees by their roots.
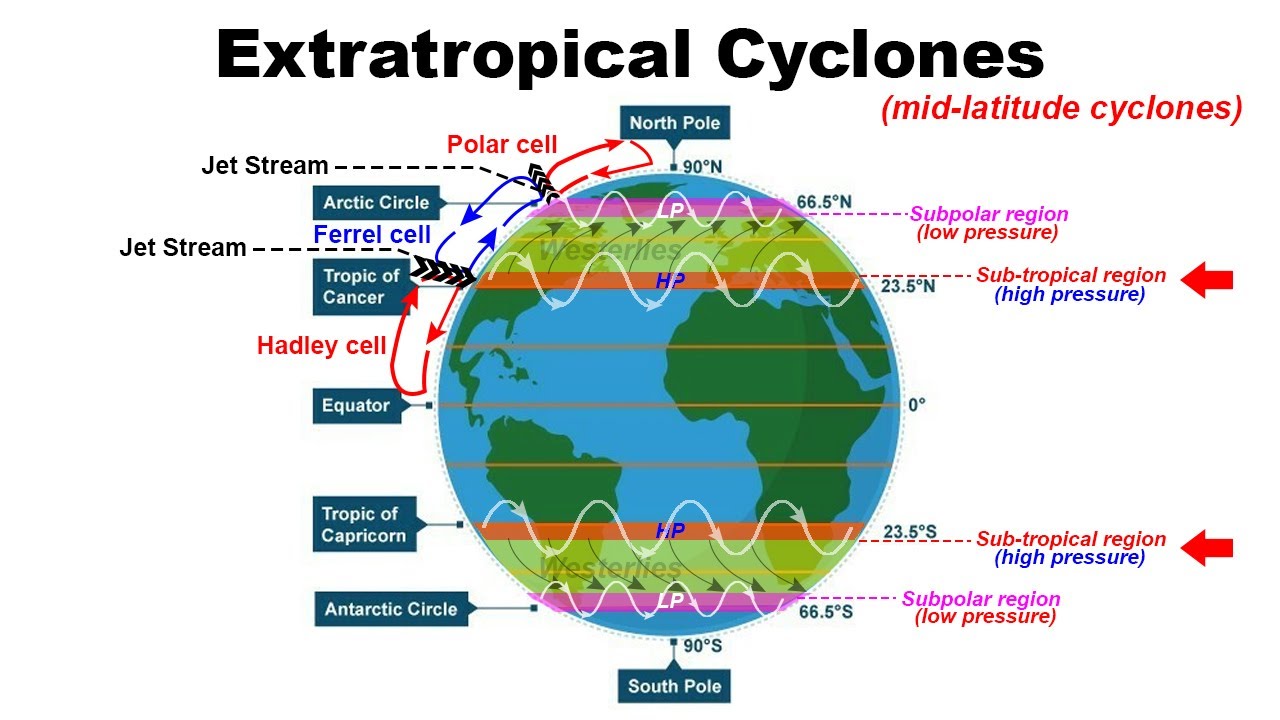
Extratropical Cyclone formation Climatology / Geography for UPSC, IAS, CDS, NDA, SSC CGL YouTube
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls.Depending on its location and strength, a tropical cyclone is referred to by different names, including hurricane (/ ˈ h ʌr ɪ k ən,-k eɪ n /), typhoon (/ t aɪ.
Atmospheric Disturbances (Cyclone and Anti Cyclone) Geography
Earth Science for Kids Weather - Hurricanes (Tropical Cyclones) What is a hurricane? A hurricane is a large rotating storm with high speed winds that forms over warm waters in tropical areas. Hurricanes have sustained winds of at least 74 miles per hour and an area of low air pressure in the center called the eye. Different Names for Hurricanes
Tropical Cyclone YASI MetService Blog
How Do Hurricanes Form? Hurricane Fran. Image made from GOES satellite data. Hurricanes are the most violent storms on Earth. People call these storms by other names, such as typhoons or cyclones, depending on where they occur. The scientific term for all these storms is tropical cyclone.

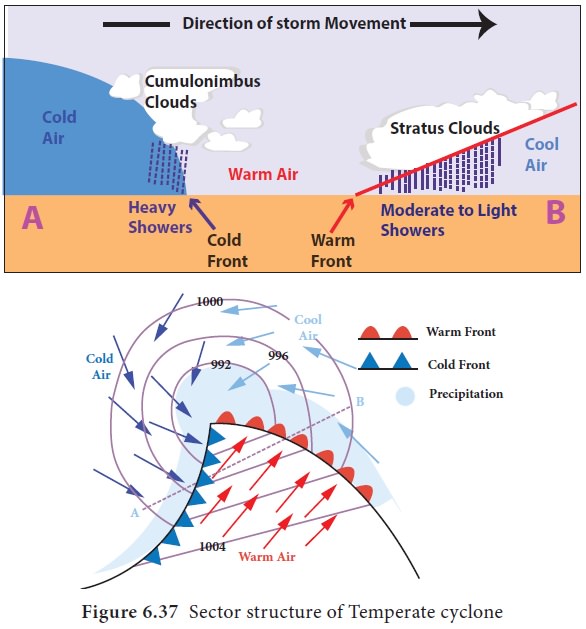
Tropical Storm Structure Geography
Definition of a tropical cyclone. Tropical cyclones are low pressure systems that form over warm tropical waters. They typically form when: atmospheric conditions are favourable, and. the sea surface temperature is above 26.5 °C. Tropical cyclones can continue for many days, even weeks.
Cyclones!!!!
Tropical Cyclone formation regions with mean tracks (courtesy of the NWS JetStream Online School) Atlantic and Eastern Pacific Hurricane Season Normal Activity. The Atlantic hurricane season runs from June 1 to November 30. The Atlantic basin includes the Atlantic Ocean, Caribbean Sea, and Gulf of Mexico. Based on a 30-year climate period from.
Paghahanda sa Bagyo Mga dapat at hindi dapat gawin bago, habang at pagkatapos ng Bagyo.
Geography Tropical Cyclones - How do they form and in what ways do they represent a hazard to people? Learning Objectives: To be able to describe the conditions leading to tropical cyclone development and the ways they represent a hazard to people. Curriculum Links: OCR Advanced GCE in Geography H483
Tropical cyclones Expert Q&A Science Media Centre
Access lesson resources for this video + more high school geography videos for free on ClickView https://clickv.ie/w/7aAw#cyclones #hurricanes #typhoons #g.

Characteristics of Cyclones GCSE Geography B Edexcel Revision Study Rocket
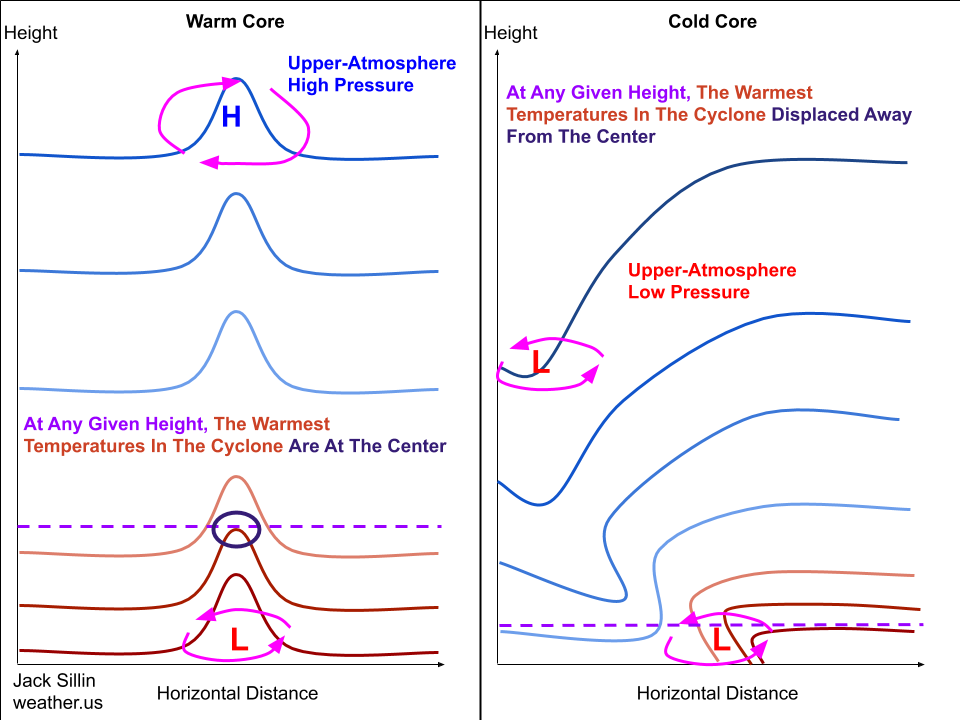
Download Image. A tropical cyclone is a warm-core low pressure system, without any front attached, that develops over the tropical or subtropical waters and has an organized circulation. These include hurricanes and typhoons. There are several favorable environmental conditions that must be in place before a tropical cyclone can form.